Jan 2023 – Oct 2023
Project assignment
Annegret Umann, Clara Kristen & Katharina Seiffarth
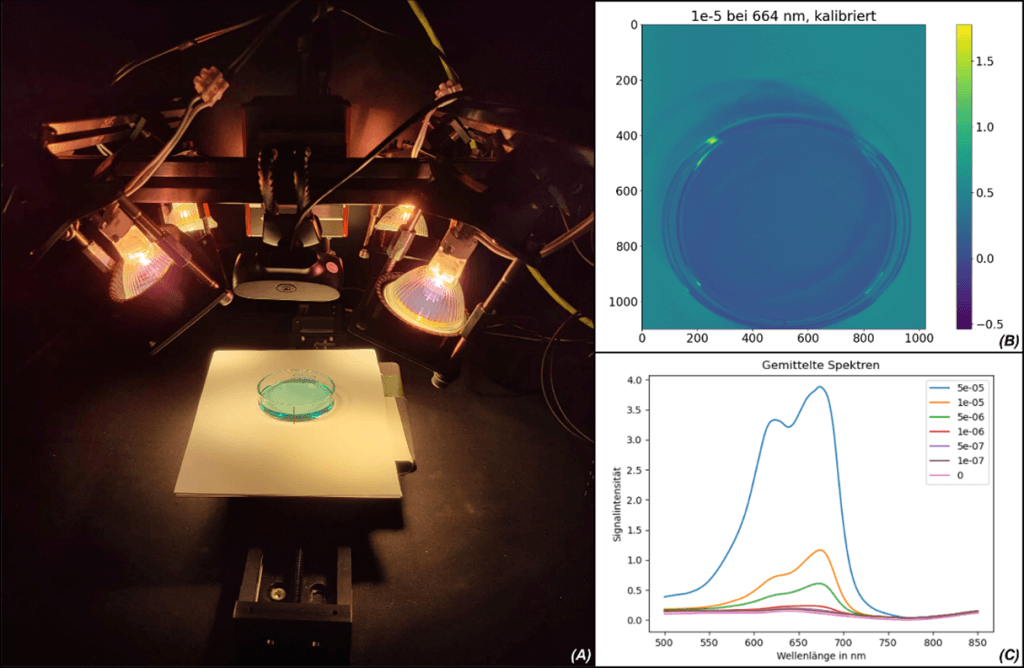
Each color of the spectrum holds a secret and encodes hidden details that can be viewed using hyperspectral imaging. This project therefore dealt with the acquisition of hyperspectral data from methylene blue solutions, their spectrum extraction and classification using machine learning pattern recognition algorithms. The “Support Vector Machine” (SVM) classifier was used to develop an automated concentration determination.
For this purpose, hyperspectral data cubes of a concentration series of methylene blue in aqueous solution were recorded, which later served as test and training data for the SVM. Python algorithms helped to calibrate and process the acquired data in order to use it effectively. A subsequent spectral principal component analysis, PCA for short, which plays an important role in dimension reduction, determined the main components of the concentration system required for classification training. By comparing actual concentrations with predictions of the trained SVM at a characteristic wavelength of 672 nm, an accuracy of 80% or 95% was achieved when the lowest concentration level was omitted.
Furthermore, the established linear dependence of the spectral response on the sample concentration results in the possibility of continuous concentration determination in the measurement range. The students thus succeeded in demonstrating discretely evaluable and reliable classification algorithms with the aid of the images from the measuring station for hyperspectral imaging.